
| Complex Numbers | Absolute Values of Complex Numbers Squared | Differences |
|---|---|---|
| 0+i | 1 | 1 |
| 1+i | 2 | 3 |
| 2+i | 5 | 5 |
| 3+i | 10 | 7 |
| 4+i | 17 | 9 |
| 5+i | 26 | 11 |
| 6+i | 37 | 13 |
| 7+i | 50 |
In the left column, consecutive integers are added to the imaginary unit i. In the middle column, the absolute values of the complex numbers are squared. In the right column are the differences of the squares of those absolute values...and have you noticed that they're consecutive odd numbers? Cool, isn't it?
| Complex Numbers | Absolute Values of Complex Numbers Squared | Differences |
|---|---|---|
| -3+i | 10 | -5 |
| -2+i | 5 | -3 |
| -1+i | 2 | -1 |
| 0+i | 1 | 1 |
| 1+i | 2 | 3 |
| 2+i | 5 | 5 |
| 3+i | 10 |
This time in the right column, we got negative differences in the top half. Of course 0+i = i, but I printed "0+i" anyway because zero(0) is an integer.
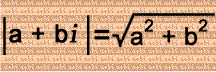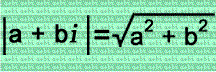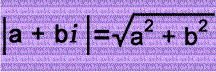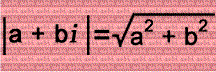
Back to Index Page Back to Math Trick Menu
© Derek Cumberbatch